-
To set a static IP address on Windows 10, open
Settings
>
Network
&
Internet
>
Wi-Fi
(or
Ethernet
), click the connection, click
“Edit,”
select
“Manual,”
turn on
“IPv4,”
and set the static IP address. -
To manually configure a static network configuration from Control Panel, open
Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter settings
, open the network adapter properties, check the
“Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4),”
click
“Properties,”
and set the static IP address. - Alternatively, you can manually set a static IP address from Command Prompt and PowerShell.
On Windows 10, setting a static IP address on your computer may be necessary for various reasons. For example, if you plan to
share files in the network
, set up a
shared printer
, enable and use
Remote Desktop
, or configure port forwarding on the router, you may need to do this.
If you don’t assign a static IP address, services or a port forwarding configuration will eventually stop working. The reason is that devices use dynamic IP addresses assigned by the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server (usually the router) by default, which can change anytime, as soon as you restart the machine or after the dynamically assigned configuration lease expires. On the other hand, a static configuration is permanent, and it’ll remain the same until you change it.
Whatever the reason it might be,
Windows 10
offers multiple ways to configure a static network configuration through the Settings app, the legacy Control Panel, and the command line using Command Prompt and PowerShell.
In this
guide
, I will teach you how to set a static IP address to a Windows 10 computer. (You can also use these instructions to
configure a static address on Windows 11
.)
-
Set a static IP address on Windows 10 from Settings
-
Set a static IP address on Windows 10 from Control Panel
-
Set a static IP address on Windows 10 from Command Prompt
-
Set a static IP address on Windows 10 from PowerShell
Set a static IP address on Windows 10 from Settings
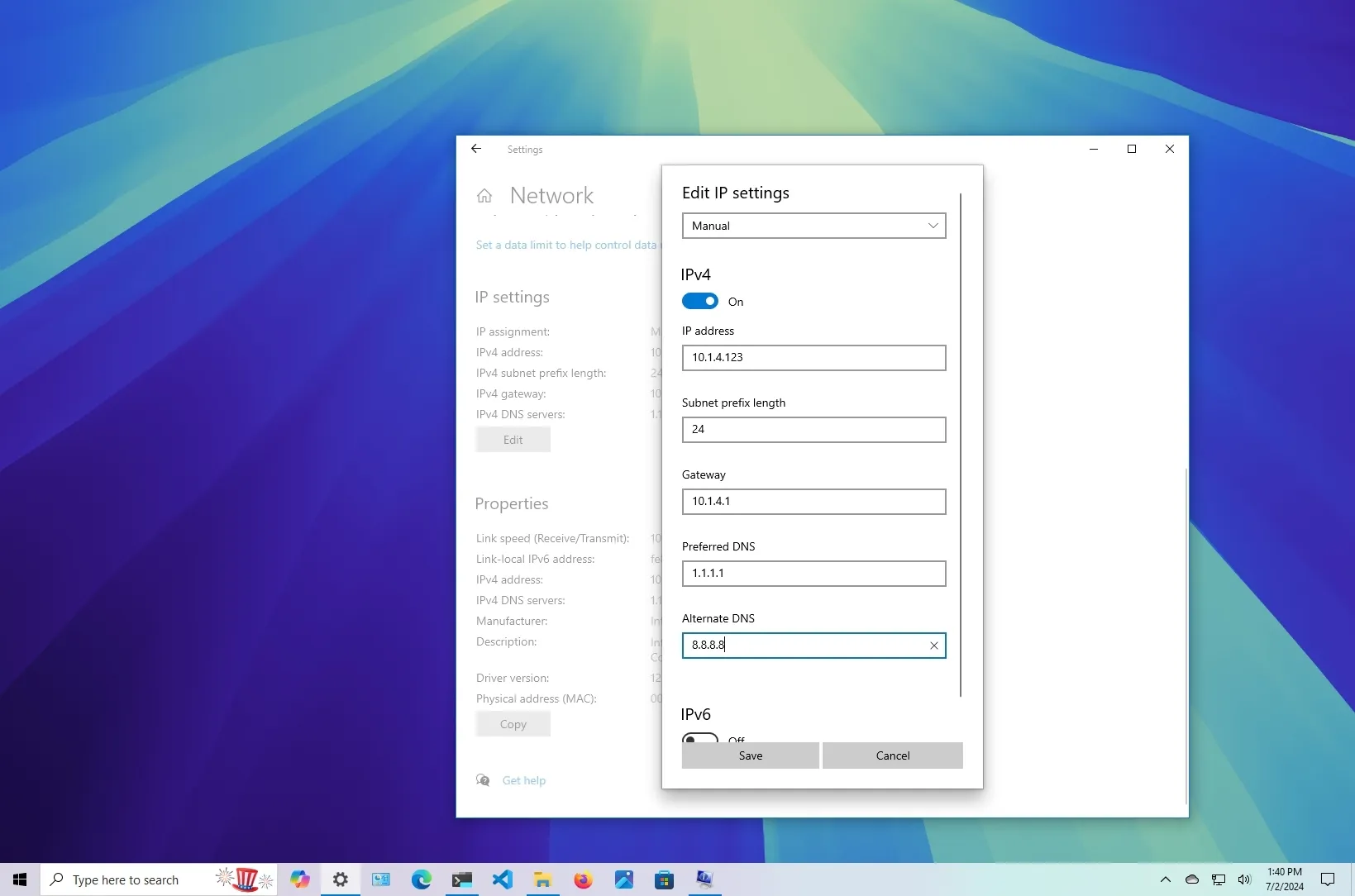
To set a static IP address manually on Windows 10, use these steps:
Open
Settings
on Windows 10.
Click on
Network & Internet
.
Click on
“Wi-Fi”
or
“Ethernet.”
Click on the current network connection.

Click the
Edit
button under the “IP settings” section.

Select the
Manual
option from the drop-down menu.
Turn on the
“IPv4”
toggle switch.

Set a static
IP address
for use on the Windows 10 computer.
Specify a
“Subnet prefix length”
(subnet mask). If your network’s subnet mask is
255.255.255.0
, then you should use the subnet prefix length
“24.”
Specify a
“Default Gateway”
address.
Specify a
“Preferred DNS”
address.
Specify an
“Alternate DNS address”
(if applicable).
Click the
Save
button.

After you complete the steps, you can test your settings using your web browser to open a website.
Check if the IP address is static or dynamic
To check if you configured the settings correctly or to tell if your device is using static or dynamic settings, use these steps:
Open
Settings
.
Click on
Network & Internet
.
Click on
Wi-Fi
or
Ethernet
.
Select the network connection.
Check whether the computer is using static (manual) or dynamic (automatic) IP address configuration under the “IP settings” section.

Once you complete the steps, you will know if your computer has been configured correctly.
Set a static IP address on Windows 10 from Control Panel
To configure a static IP from the Control Panel, use these steps:
Open
Control Panel
.
Click on
Network and Internet
.
Click on
Network and Sharing Center
.
Click the
Change adapter settings
option on the left navigation pane.

Right-click the
Wi-Fi
or
Ethernet
adapter and select the
Properties
option.
Select the
“Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)”
option.
Click the
Properties
button.

Select the
“Use the following IP address”
option.
Set the static
IP address
for the adapter – for example,
10.1.2.220
.
Specify a
Subnet mask
for the network, such as
255.255.255.0
.
Specify a
Default gateway
(which is usually the router’s IP address).
Confirm the
“Preferred DNS server”
address under the “Use the following DNS server addresses set Preferred DNS server” section. (It is Usually your router’s IP address or the server IP address that provides the DNS resolution.)
(Optional) Specify an
Alternative DNS server.
(The computer will use this address if it cannot reach the preferred DNS server.)
Click the
OK
button.

Click the
Close
button again.
Once you complete the steps, you can open your web browser and load a website to see if the configuration works.
Set a static IP address on Windows 10 from Command Prompt
To set a static IP address manually from Command Prompt, use these steps:
Open
Start
.
Search for
Command Prompt
, right-click the top result, and select the
Run as administrator
option.
Type the following command to see your current networking configuration and press
Enter
:
Under the network adapter, note the name of the adapter as well as the following information in these fields:
-
IPv4
-
Subnet mask
-
Default Gateway
-
DNS Servers

Type the following command to assign a static IP address on Windows 10 and press
Enter
:
In the above command, replace
“Ethernet0”
with the name of your network adapter. Change
“10.1.4.220 255.255.255.0 10.1.4.1”
with the device IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway address corresponding to your network configuration.
Type the following command to set a DNS server address and press
Enter
:
In the command, make sure to change
“Ethernet0”
with your adapter’s name and
“10.1.4.1”
with the DNS server address of the network.
Type the following command to set an alternate DNS server address and press
Enter
:
In the command, replace
“Ethernet0”
with your adapter’s name and
“8.8.8.8”
with an alternate DNS server address.

(Optional) Type the following command, and if the
“DHCP Enabled”
is set to
“No,”
then the static configuration has been applied and press
Enter
:
After you complete the steps, you can test the new configuration using the
ping
command (for example
ping google.com
) to see if the internet is working. Alternatively, you can open a website to see if the configuration works.
Set a static IP address on Windows 10 from PowerShell
Windows 10 also includes the PowerShell command line console that allows you to use the “NetTCPIP” module to manage networking settings, including the ability to change your computer’s IP address settings. Microsoft recommends using this command-line method instead of
netsh
.
To set a static IP address on Windows 10 from PowerShell, use these steps:
Open
Start
.
Search for
PowerShell
, right-click the result, and select the
Run as administrator
option.
Type the following command to view your current network configuration and press
Enter
:
After running the command, note the following information:
-
InterfaceIndex
-
IPv4Address
-
IPv4DefaultGateway
-
DNSServer

Type the following command to set a static IP address and press
Enter
:

In the command, replace the
“InterfaceIndex”
number
(5)
with the corresponding number of your adapter. Change
“IPAddress”
with the static IP address you want to assign to your device. If necessary, change
PrefixLength
(subnet mask) with the correct bit number. Typically, on a home network, the setting is
“24.”
Also, change the
“DefaultGateway”
option with the network’s default gateway address.
Type the following command to assign a DNS server address and press
Enter
:

If you need to set a secondary DNS server address, use a comma to use the same command with another address. For example:
In the command, replace the
“InterfaceIndex”
number
(5)
with your network adapter’s corresponding number. Also, change
“ServerAddresses”
with the DNS IP address.
(Optional) Type the following command, and if the
“PrefixOrigin”
and
“SuffixOrigin”
are set to
“Manual”
in the output, then the static configuration has been applied, and press
Enter
:
After you complete the steps, you can test the new configuration by opening your web browser and navigating a website.
Whatever method you use, assigning an IP address within the
network range
and
outside of the DHCP server scope
is recommended to allow proper connectivity and prevent address conflicts. If multiple devices share the same address, this will cause a networking conflict, preventing connection to the internet.
Although there are two main standards in use today, including
IPv4
and
IPv6
, version 4 is still the most widely used, especially in local networks, and for this reason, this guide focuses on setting up IPv4.
Update July 4, 2024:
This guide has been updated to ensure accuracy and reflect changes to the process.